Table of Contents
Introduction
Vitamin B9, also known as folate or folic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that is essential for the proper functioning of the human body. It plays a crucial role in DNA synthesis, cell division, and red blood cell formation. In this article, we will explore the importance of Vitamin B9, its health benefits, symptoms of deficiency, sources, recommended daily intake, and how to supplement with it.
Health Benefits of Vitamin B9
Fetal development
Vitamin B9 is particularly important for pregnant women, as it is essential for fetal development. Adequate intake of Vitamin B9 during pregnancy can reduce the risk of birth defects such as spina bifida and anencephaly.
Reducing risk of birth defects
In addition to reducing the risk of birth defects, Vitamin B9 can also lower the risk of premature birth and low birth weight.
Supporting brain function
Vitamin B9 is essential for proper brain function and may help prevent cognitive decline in older adults.
Preventing anemia
Vitamin B9 plays a role in red blood cell formation and can help prevent megaloblastic anemia.
Lowering risk of heart disease
Studies have shown that Vitamin B9 can lower homocysteine levels, an amino acid linked to an increased risk of heart disease.
Promoting healthy skin
Vitamin B9 is essential for healthy skin, as it plays a role in the formation of new skin cells.
Symptoms of Vitamin B9 Deficiency
Megaloblastic anemia
Megaloblastic anemia is a type of anemia that occurs when red blood cells are larger than normal, which can lead to fatigue, weakness, and shortness of breath.
Fatigue and weakness
Vitamin B9 deficiency can cause fatigue and weakness, as it plays a role in energy production.
Irritability and depression
Low levels of Vitamin B9 have been linked to irritability and depression.
Digestive problems
Vitamin B9 deficiency can cause digestive problems such as nausea, diarrhea, and loss of appetite.
Who is at Risk of Vitamin B9 Deficiency?
Pregnant women
Pregnant women require higher amounts of Vitamin B9 to support fetal development. However, many women do not consume enough Vitamin B9 during pregnancy, putting them at risk of deficiency.
People with digestive disorders
Conditions such as celiac disease, inflammatory bowel disease, and Crohn’s disease can affect the body’s ability to absorb Vitamin B9, leading to deficiency.
Alcoholics
Excessive alcohol consumption can interfere with the absorption of Vitamin B9, leading to deficiency.
People taking certain medications
Certain medications such as anticonvulsants, methotrexate, and sulfasalazine can interfere with the body’s ability to absorb Vitamin B9.
Elderly individuals
As we age, our ability to absorb nutrients decreases, which can increase the risk of Vitamin B9 deficiency.
Recommended Daily Intake of Vitamin B9
The recommended daily intake of Vitamin B9 varies depending on age and gender. For adults, the recommended daily intake is 400-600 micrograms (mcg) per day. However, pregnant women require 600-800 mcg per day, while breastfeeding women require 500-600 mcg per day.
Factors such as alcohol consumption, smoking, and certain medications can increase the need for Vitamin B9.
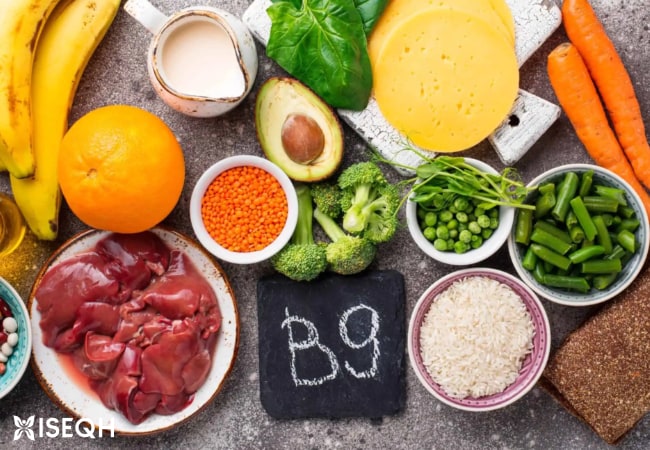
Food Sources of Vitamin B9
There are many food sources of Vitamin B9, including:
Dark leafy greens
Examples include spinach, kale, and collard greens.
Legumes
Examples include lentils, chickpeas, and black beans.
Fruits and vegetables
Examples include citrus fruits, broccoli, and asparagus.
Animal products
Examples include liver, beef, and eggs.
Fortified foods
Many cereals, breads, and other grain products are fortified with Vitamin B9.
How to Supplement with Vitamin B9
If you are unable to consume enough Vitamin B9 through diet alone, supplements may be necessary. There are two types of Vitamin B9 supplements: folate and folic acid.
Folate is the natural form of Vitamin B9 found in food, while folic acid is the synthetic form found in supplements and fortified foods. Both forms are effective at increasing Vitamin B9 levels in the body.
The recommended dosage of Vitamin B9 supplements varies depending on age and gender. For adults, the recommended dosage is 400-1000 mcg per day. However, pregnant women may require higher dosages.
Potential side effects of Vitamin B9 supplements include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal cramping.
Conclusion
Vitamin B9 is a crucial nutrient that plays a vital role in many functions of the human body. Adequate intake of Vitamin B9 can help prevent birth defects, support brain function, prevent anemia, and lower the risk of heart disease. Deficiency of Vitamin B9 can lead to a variety of symptoms, including megaloblastic anemia, fatigue, and irritability. To ensure you are getting enough Vitamin B9, consume a balanced diet rich in folate-rich foods, and consider supplementation if necessary.
FAQs
Can taking too much Vitamin B9 be harmful?
While it is possible to overdose on Vitamin B9, it is rare. However, high doses of Vitamin B9 can mask the symptoms of a Vitamin B12 deficiency, which can lead to nerve damage.
Is it possible to get enough Vitamin B9 through diet alone?
Yes, it is possible to consume enough Vitamin B9 through a balanced diet rich in folate-rich foods. However, supplementation may be necessary.
Can Vitamin B9 help prevent birth defects?
Yes, adequate intake of Vitamin B9 during pregnancy can help prevent birth defects, particularly neural tube defects.
Can Vitamin B9 help prevent heart disease?
Yes, research suggests that adequate intake of Vitamin B9 may help lower the risk of heart disease.
Can Vitamin B9 supplements cause any side effects?
Potential side effects of Vitamin B9 supplements include nausea, diarrhea, and abdominal cramping. However, these side effects are rare and generally only occur with high doses.