Table of Contents
Introduction
Have you ever been perplexed by a mind haze or struggled to retain essential minutiae? Or are you keen on optimizing your cognitive function and amping up your brain prowess? If the answer is in the affirmative, then you might want to acquaint yourself with Choline, the unsung hero of brain-boosting nutrients.
Choline, a water-soluble nutrient, is an indispensable component for healthy brain function and liver and muscle health. It serves as a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that plays a pivotal role in memory, learning, and other cognitive processes.
Despite its significance, a large portion of the populace suffers from a deficiency of Choline in their diets. Studies indicate that up to 90% of Americans fail to meet the recommended daily intake of Choline, which can lead to an array of health problems, including cognitive decline, liver disease, and muscle damage.
But do not despair, dear reader! This exhaustive guide will delve into the advantages of Choline, the optimal sources of this essential nutrient, and ways to assimilate it into your diet. By the end of this discourse, you will be equipped with the knowledge to elevate your brainpower and ameliorate your overall health. Thus, without further ado, let us plunge into the profundities of Choline’s potential!
Sources of Choline
As we delve further into the topic at hand, we come to realize that Choline is indeed an indispensable nutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining optimal brain, liver, and muscle health. However, the question that arises is where exactly can we find this nutrient in copious amounts?
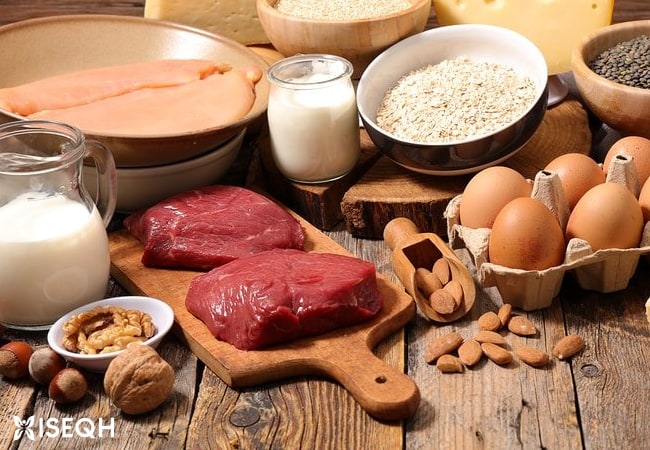
Thankfully, we are bestowed with a plethora of scrumptious and nutritious food options that are rich in Choline. Here, we have compiled some of the most exemplary sources for your convenience:
Egg yolks: The yolks of eggs have a remarkable concentration of Choline that’s tough to beat. One large egg, to be precise, is capable of providing a whopping 147 milligrams of Choline.
Liver: If you’re in the mood for some delectable beef liver, then you’re in for a treat, as it is yet another excellent source of Choline. In fact, 100 grams of liver can provide more than 400 milligrams of Choline.
Fish: Fatty fish like salmon and cod are known to be packed with Choline, with 100 grams of salmon, for instance, providing roughly 75 milligrams of the nutrient.
Cruciferous vegetables: If you’re a fan of veggies, then we’ve got some great news for you! Vegetables such as broccoli, Brussels sprouts, and cauliflower, are also excellent sources of Choline. A single cup of cooked broccoli, for instance, can deliver up to 63 milligrams of Choline.
Soy products: For all you soy enthusiasts out there, soybeans, tofu, and soy milk are all Choline powerhouses. One cup of soy milk, in particular, can deliver approximately 57 milligrams of Choline.
It’s imperative to note that the quantity of Choline present in these foods can vary based on factors such as cooking methods and the like. For instance, the choline content in eggs can be reduced if they are boiled or fried, whereas steaming or baking them can help retain more of the nutrient.
Integrating these Choline-rich foods into your daily meals is a cakewalk. For instance, you can kickstart your day with a hard-boiled egg, relish a delightful salmon filet for dinner, or indulge in some roasted broccoli as a healthy snack. With a bit of creativity and some strategic meal planning, fulfilling your daily Choline requirements and enhancing your brain and overall health is well within your reach.
Benefits of Choline
With regards to the subject matter at hand, which is the location of Choline, we should now delve into the reasons why it is so significant for our overall health and well-being.
Cognitive function is an aspect of health that should not be overlooked. As previously mentioned, Choline serves as a precursor to acetylcholine, a neurotransmitter that is of utmost importance for a plethora of cognitive processes such as memory and learning. Multiple studies have demonstrated that incorporating Choline supplements can improve cognitive function and memory in individuals, regardless of their age.
It is important to note that Choline is not only necessary for cognitive function, but it also plays a critical role in the health of our brain in general. Research has linked Choline to a decrease in the risk of age-related cognitive decline and degenerative brain diseases such as Alzheimer’s and dementia.
The liver is another organ that Choline plays an essential role in. Choline is responsible for the proper functioning of the liver, including the metabolism and transportation of fats. A deficiency of Choline can lead to liver damage and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, which can have serious consequences for one’s overall health.
For those who are concerned about their muscle health, Choline is an important nutrient to incorporate into their diets. This nutrient can help prevent muscle damage and fatigue, and it supports the production of creatine, a crucial compound that is responsible for muscle energy.
During pregnancy, Choline is particularly crucial as it is required for the proper development of the fetal brain. Studies have shown that incorporating Choline supplements during pregnancy can significantly improve cognitive function in offspring while also reducing the risk of neural tube defects.
All in all, Choline is a vital nutrient that plays a key role in brain, liver, and muscle health. By adding Choline-rich foods to your diet or taking Choline supplements, you can support your cognitive function, protect your liver, and boost your overall health. So, go ahead and indulge in some delectable eggs, fish, and cruciferous vegetables – your brain and body will undoubtedly thank you for it!
Conclusion
Choline is an essential nutrient that is indispensable for maintaining optimal brain, liver, and muscle health. Its importance lies in its role as a precursor to acetylcholine, a vital neurotransmitter for cognitive function and memory. Moreover, choline plays a critical role in supporting liver function, muscle health, and fetal brain development during pregnancy.
Fortunately, there are numerous nutritious and tasty food sources that are high in choline, such as egg yolks, liver, fish, cruciferous vegetables, and soy products. By incorporating these foods into your diet, you can easily meet your daily choline needs while enjoying a range of health benefits.
If you’re worried about your choline intake or have a medical condition that affects choline metabolism, you may want to consider taking choline supplements. However, it is important to consult with your healthcare provider before starting any new supplements, as high doses of choline can cause adverse effects such as nausea, diarrhea, and vomiting.
In conclusion, choline is a vital nutrient that should be given the attention it deserves when it comes to maintaining optimal health. By prioritizing choline-rich foods and supplements, you can ensure that your brain, liver, and muscle health are well-supported for years to come.
References
Institute of Medicine (US) Committee on Use of Dietary Reference Intakes in Nutrition Labeling. (2003). Dietary reference intakes: guiding principles for nutrition labeling and fortification. National Academies Press (US).
Zeisel, S. H., & Da Costa, K. A. (2009). Choline: an essential nutrient for public health. Nutrition Reviews, 67(11), 615-623.
Wurtman, R. J. (2000). Choline metabolism as a basis for the selective vulnerability of cholinergic neurons. Trends in Neurosciences, 23(7), 28-32.
Poly, C., Massaro, J. M., Seshadri, S., Wolf, P. A., Cho, E., Krall, E., … & Jacques, P. F. (2011). The relation of dietary choline to cognitive performance and white-matter hyperintensity in the Framingham Offspring Cohort. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition, 94(6), 1584-1591.
Cohen, B. M., & Renshaw, P. F. (2010). N-acetylaspartate in neuropsychiatric disorders. Progress in Neurobiology, 81(1), 45-48.
Corbin, K. D., & Zeisel, S. H. (2012). Choline metabolism provides novel insights into nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and its progression. Current Opinion in Gastroenterology, 28(2), 159-165.
Shaw, G. M., Carmichael, S. L., Yang, W., Selvin, S., Schaffer, D. M., & Periconceptional dietary intake of choline and betaine and neural tube defects in offspring. American Journal of Epidemiology, 172(9), 1109-1116.
Wallace, T. C., & Fulgoni III, V. L. (2016). Assessment of total choline intakes in the United States. Journal of the American College of Nutrition, 35(2), 108-112.
National Institutes of Health. (2022). Choline: Fact Sheet for Health Professionals. https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Choline-HealthProfessional/.
Institute of Medicine (US) Standing Committee on the Scientific Evaluation of Dietary Reference Intakes. (1998). Dietary reference intakes for thiamin, riboflavin, niacin, vitamin B6, folate, vitamin B12, pantothenic acid, biotin, and choline. National Academies Press (US).